February is expected to be a fascinating month for three countries —USA, China, and the United Arab Emirates—as three separate Mars missions approach the red planet. Out of the three, The Hope craft launched by the United Arab Emirates has successfully entered the orbit of Mars recently. Moreover, China’s Tainwen-1 and US’s Mars 2020 craft are also heading for the red planet with orbiters and rovers.
-
The Emirates Mars Mission
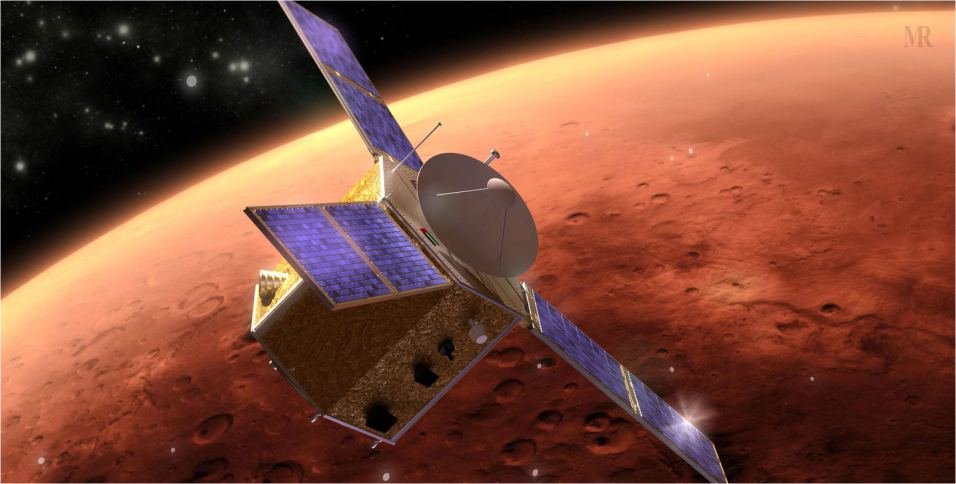

The Emirates Mars mission launched its probe named Hope on July 20, 2020 from Tanegashima Space Centre, Japan. Hope is the first Arab Interplanetary mission. It aims to provide scientists with a complete picture of the Martian Atmosphere. And they promise to share the data. On February 9, 2021, Hope began the Mars Orbit Insertion (MOI).
One of the EMM spokesperson said, “The burn was always going to be rather nerve-wracking 27 minutes. That’s where the orbiter has to burn off fuel and slow down to meet its target.” The operation was fully-autonomous, with the probe 11 minutes’ radio-time away from the earth. Hope used six thrusters to provide 650 Newton of power. Firing the thrusters for that long can expose the spacecraft to a lot of stress, from vibrations through to heat. However, all went well as the Hope probe now starts a two-Earth year mission and the UAE has become the first Arab Nation to get to Mars.
Related: Meet the first Private Space Crew to travel Space Station
-
Tainwen-1

China’s first independent Mars mission, Tainwen-1 was launched on July 23, 2020, from the Wenchang Space Launch Centre in Hainan province. Tainwen-1 is also expected to enter the Martian orbit during the second week of February. In fact, it is expected that the Chinese probe will make it the day after the EMM –and two days before the Chinese New Year.
The spacecraft will conduct a braking operation to decelerate its speed to a point at which it can be captured by Mars’ gravity. Much like the EMM, Tainwen-1 will survey the Martian atmosphere. The main part of this mission is scheduled for May when China aims to soft-land a rover in the southern part of Mars’ Utopia Planitia
-
Perseverance and Ingenuity
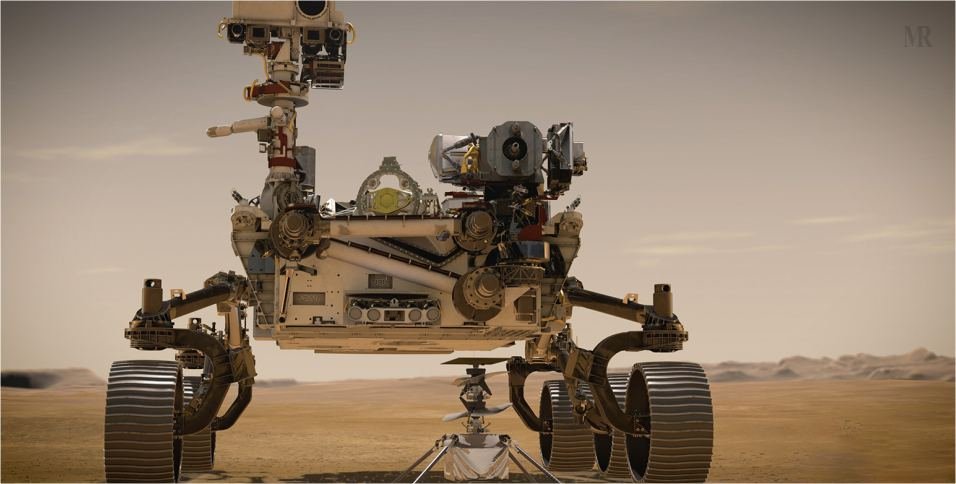
The USA’s latest Mars Mission involves a new rover called Perseverance and a helicopter called Ingenuity. Ingenuity is strapped to the belly of the rover. The rover is due to land on February 18 at a place called Jezero Crater. It will descend through the Martian atmosphere at a speed of about 20,000 kmph.
The rover will be slowed with a parachute and a powered descent to about 3.2 kph. Then, a large sky crane will lower the rover on three bridle cards until it lands softly on six wheels. NASA describes Perseverance as a “robotic astrobiologist” as it is the largest and most sophisticated rover ever sent to the Mars’ surface.
Also Read: SpaceX’s Starlink decides to go for IPO
















