Lesson planning is a crucial aspect of effective teaching. It involves organizing and structuring learning activities to engage students and achieve specific educational goals.
However, crafting comprehensive and engaging lesson plans can be a daunting task for many educators. In this ultimate guide to lesson planning, we will explore a variety of tips and strategies to help teachers create impactful lesson plans that promote student engagement and learning.
- The Significance of Choosing the Right Lesson Planner:
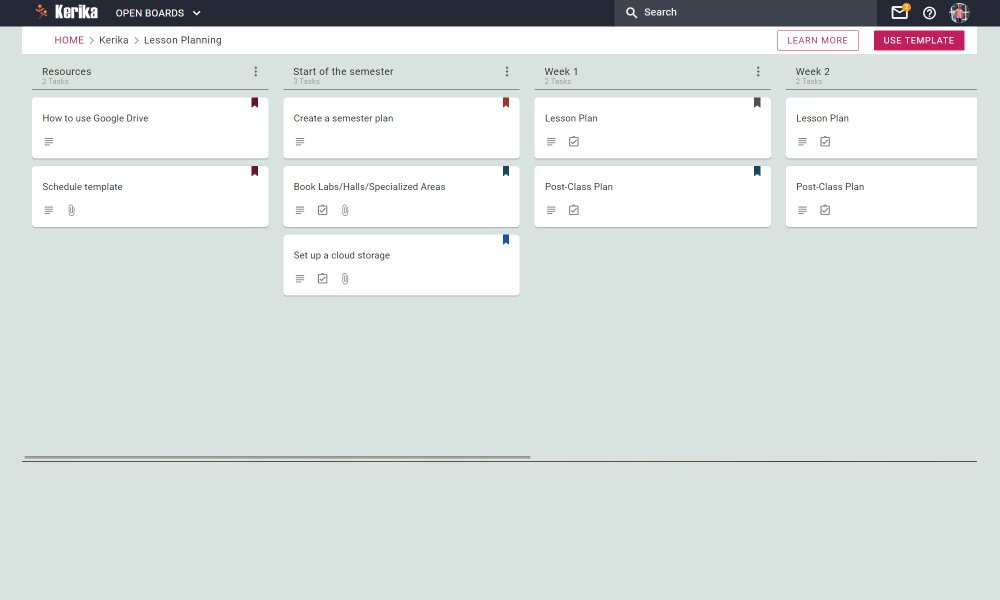
Choosing the right lesson planner is important as it directly impacts your ability to organize teaching materials efficiently and save time in the long run. Kanban tools have gained popularity among teachers due to their visual and flexible nature. There are many tools available in the market like Clickup and Trello. But if you’re looking for a cost-effective tool that caters specifically to educators, Kerika is the standout choice.
- Lesson Planning Templates: Kerika provides a dedicated lesson planning template designed explicitly for teachers like you.
- Streamlined Lesson Organization: You add your students as team members, or give them view-only access to share more details about your classes and study materials.
- Integration with Google Drive: many schools have adopted Google Apps, and in choosing a tool it’s important to make sure it integrates very well with Google Docs, Google Drive, etc. Here, Kerika stands out from the alternatives, because if you sign up using your Google ID, your project files are stored safely in your own Google Drive. Another big advantage is that Kerika lets you create new Google Docs, Slides, Sheets, etc. from inside the app, and have them shared automatically with the right people.
- Understand Your Objectives: Before diving into the lesson planning process, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of your objectives. Identify what you want your students to learn or achieve by the end of the lesson. Define specific learning outcomes that align with the curriculum and cater to the needs of your students.
- Know Your Students: Effective lesson planning requires knowing your students well. Consider their interests, learning styles, and abilities when designing your lessons. Differentiate instruction to accommodate diverse student needs and create a student-centered learning environment.
Some ways to do this are:
- Survey your students about their hobbies, passions, or preferences before designing your lessons
. - Use examples, scenarios, or problems that relate to students’ lives or experiences.
- Allow students to choose from different options or formats for learning activities or assessments.
- Use Backward Design: Adopt the backward design approach, where you start planning by identifying the desired outcomes and then work backward to determine the instructional strategies and assessments. This approach ensures that your lessons are focused on achieving specific learning goals.
One of the most widely used strategies for lesson planning is the backward design model proposed by Wiggins and McTighe are:
- Identify the desired results: what are the overall learning goals and standards that you want students to achieve?
- Determine the acceptable evidence: what are the criteria and methods that you will use to measure students’ achievement of the desired results?
- Plan the learning experiences and instruction: what are the activities and resources that you will use to help students achieve the desired results?
- Incorporate Active Learning: Engage your students by incorporating active learning strategies into your lesson plans. Encourage student participation through group discussions, hands-on activities, role-plays, and problem-solving tasks. Active learning enhances comprehension, critical thinking, and retention of knowledge.
Active learning has many benefits for students and teachers, such as:
- Improving student performance and decreasing failure rates, especially for
- students from underrepresented and excluded communities.
- Enhancing student comprehension, critical thinking, and retention of knowledge.
- Developing student skills such as collaboration, communication, and problem-solving.
- Increasing student motivation, interest, and satisfaction with learning.
- Providing feedback for teachers to assess student understanding and adjust instruction accordingly.
- Include Formative Assessments: Integrate formative assessments throughout your lessons to gauge student understanding and provide immediate feedback. Use a variety of assessment techniques, such as:
- Think-pair-share: Ask students to think about a question or problem individually, then pair up with a partner to discuss their ideas, then share their responses with the whole class.
- Peer instruction: Ask students to answer a multiple-choice question individually using clickers or other devices, then have them discuss their answers with their peers and vote again, then explain the correct answer and the reasoning behind it.
- Exit ticket: Ask students to write a brief response to a question or prompt at the end of the lesson and hand it in before they leave. Review the responses to assess student understanding and plan for the next lesson.
- Observation: Observe students as they work on an activity or task and take notes on their performance, behavior, or attitudes. Use the notes to provide feedback or adjust instruction as needed.
- Self/peer assessment: Ask students to assess their own or their peers’ work using a rubric or checklist. Have them identify strengths, areas for improvement, and suggestions for revision.
- Plan for Differentiation: Recognize and accommodate the diverse needs of your students by incorporating differentiation strategies into your lesson plans. Provide opportunities for advanced learners to extend their knowledge while offering additional support for struggling students.
Differentiated instruction promotes inclusivity and ensures that every student can actively participate and succeed.
- Create a Visual Lesson Plan: Consider creating a visual representation of your lesson plan using charts, tables, or infographics. A visual layout helps you organize your thoughts and makes it easier to communicate your lesson objectives, activities, and assessments. It also serves as a valuable reference tool during instruction.
Some tips for creating a visual lesson plan are:
- Use colors, fonts, icons, and images that are consistent, relevant, and appealing.
- Use headings, labels, legends, and captions to provide clear and concise information.
- Use charts, tables, or infographics to summarize or compare data or information.
- Use diagrams, maps, or timelines to show relationships or sequences of events or processes.
- Use symbols, arrows, or lines to highlight connections or transitions between different parts of your lesson plan.
(Kerika’s Whiteboards feature can help with this: you can incorporate your Whiteboards directly into the Lesson Plan.)
- Collaborate with Colleagues: Collaboration with fellow teachers can provide fresh perspectives and ideas for lesson planning. Share resources, exchange lesson plan templates, and discuss teaching strategies with your colleagues. Collaborative planning allows for collective expertise and fosters a supportive professional learning community.
Some tips for collaborative planning are:
- Establish clear goals and expectations for the collaboration process and outcomes.
- Choose a suitable format and frequency for the collaboration meetings or sessions.
- Assign roles and responsibilities to each team member based on their strengths and interests.
- Use a variety of sources and methods to gather data and evidence for lesson planning.
- Provide constructive feedback and celebrate successes with your team.
This is another area where Kerika proves invaluable, since it makes it really easy to share your lesson plans with colleagues. If there are folks that you want to help with revising your plans, you can add them as Team Members to your Lesson Plan Board, and they will be able to make changes. And if there are folks who just need to be in the loop, add them as Visitors and they will always have a real-time view of the Lesson Plan.
- Reflect and Revise: After delivering your lesson, take the time to reflect on its effectiveness. Consider what worked well and what could be improved. Use student feedback and assessment data to inform your future lesson planning and make necessary revisions for ongoing improvement.
In conclusion, lesson planning is an ongoing process that requires careful thought, creativity, and flexibility. By implementing the tips and strategies outlined in this ultimate guide, teachers can create engaging and effective lesson plans that facilitate meaningful learning experiences for their students. Remember to adapt these suggestions to suit your specific teaching context and the unique needs of your learners. Happy planning!
ALSO READ: Digital Education Tools for Teachers and Students
















